Design with the user
13 November 2014
1. User-centered Design, User-experience design, Co-Design
2. Lead users, Open Innovation and Open Source
1. User-centered, User-experience, Co- Design
Traditional view of design
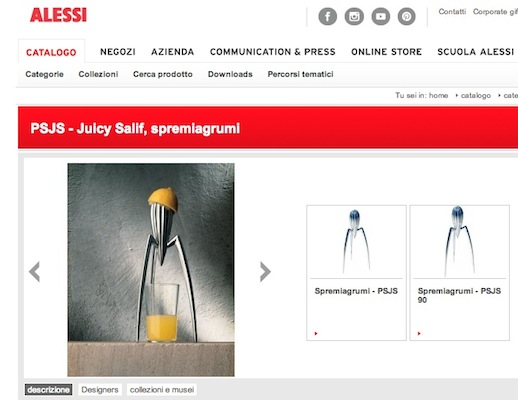
Source: http://www.alessi.it/it/3/1055/accessori-da-cucina/juicy-salif-spremiagrumi
Limitations...
Any customer can have a car painted any colour that he wants so long as it is black.
Henry Ford
Approaches...
- Marketing (market pull)
- Technology (technology push)
- Mass-customization
- ...
- Human-centered Design
Human-centered Design
an approach to systems design and development that aims to make interactive systems more usable by focusing on the use of the system and applying human factors/ergonomics and usability knowledge and techniques
Source: ISO 9241-210
ISO 9241-210: Abstract
ISO 9241-210:2010 provides requirements and recommendations for human-centred design principles and activities throughout the life cycle of computer-based interactive systems. It is intended to be used by those managing design processes, and is concerned with ways in which both hardware and software components of interactive systems can enhance human–system interaction.
Source: ISO 9241-210
ISO 9241-210: Recommendations
- The adoption of multidisciplinary skills and perspectives
- Explicit understanding of users, tasks and environments
- User-centred evaluation driven/refined design
- Consideration of the whole user experience
- Involvement of users throughout design and development
Source: ISO 9241-210
Roots: Human-computer Interaction
Human–computer interaction (HCI) involves the study, planning, and design of the interaction between people (users) and computers. It is often regarded as the intersection of computer science, behavioral sciences, design and several other fields of study.
Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human%E2%80%93computer_interaction
Roots: Human-computer Interaction
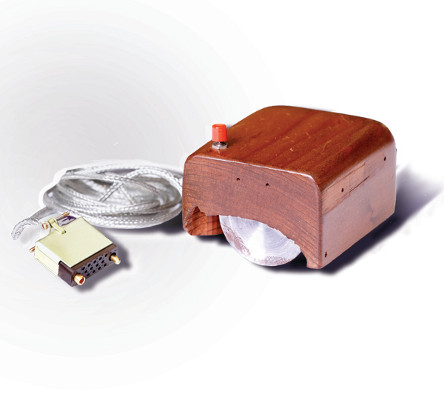

... to Social Innovation
... to a Kit for NGO

Source: http://www.ideo.com/work/human-centered-design-toolkit/
... to an online platform
Source: http://www.hcdconnect.org/
... to a no-profit initiative
Source: http://www.hcdconnect.org/
... to an online course
Source: http://vimeo.com/68659872
Roots: Participatory Design
Participatory design (known before as cooperative design) is an approach to design attempting to actively involve all stakeholders (e.g. employees, partners, customers, citizens, end users) in the design process in order to help ensure the product designed meets their needs and is usable.
User-centered Design
User-centered design (UCD) is an approach to design that grounds the process in information about the people who will use the product. UCD processes focus on users through the planning, design and development of a product.
Usability Professionals' Association
Source: http://www.usabilityprofessionals.org/usability_resources/about_usability/what_is_ucd.html
User-centered Design: Principles

Gould, J. D., & Lewis, C. (1985). Designing for usability: key principles and what designers think. Commun. ACM, 28(3), 300–311. doi:10.1145/3166.3170
User-centered Design: The design process from ISO-13407
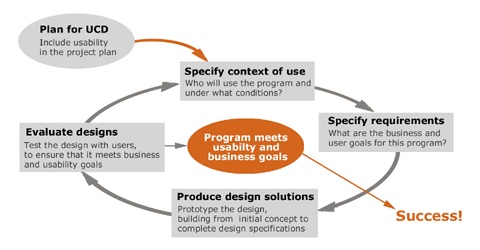
Source: http://www.wqusability.com/articles/language-usability-tekom-proceedings.html
User-centered Design: models
design model vs. user model
as understood by designers vs. as understood by users
Source: Rizzo, F. (2009). Strategie di co-design : teorie, metodi e strumenti per progettare con gli utenti. Milano: F. Angeli.
User-centered Design: Usability
- easiness of learning
- efficiency of the user
- easiness of memorizing
- few errors
- user satisfaction
Source: Mack, R. L., & Nielsen, J. (1994). Usability inspection methods. Wiley & Sons.
A nice book about usability...
Source: Tullis, T., & Albert, W. (2013). Measuring the User Experience: Collecting, Analyzing, and Presenting Usability Metrics (Interactive Technologies) (2 edition.). Morgan Kaufmann.
User-centered Design: Cognitive Psychology
Source: Norman, D. A. (2013). Design of everyday things. [S.l.]: Basic Books.
Cognitive Psychology: affordances
- Give visibility of all the functional parts
- Give a good mapping between command and result
- Give affordances and constraints
- Give feedback
- Give a good conceptual model
- Simplify tasks
Source: Norman, D. A. (2013). Design of everyday things. [S.l.]: Basic Books.
Cognitive Psychology: affordances
An affordance is a quality of an object, or an environment, which allows an individual to perform an action by suggesting the action to be taken.Source: Norman, D. A. (2013). Design of everyday things. [S.l.]: Basic Books.
Cognitive Psychology: constraints
- Physical
- Semantic
- Cultural
- Logic
Source: Norman, D. A. (2013). Design of everyday things. [S.l.]: Basic Books.
Tools: Personas

Tools: Scenario / Storyboard
... more tools: a toolkit
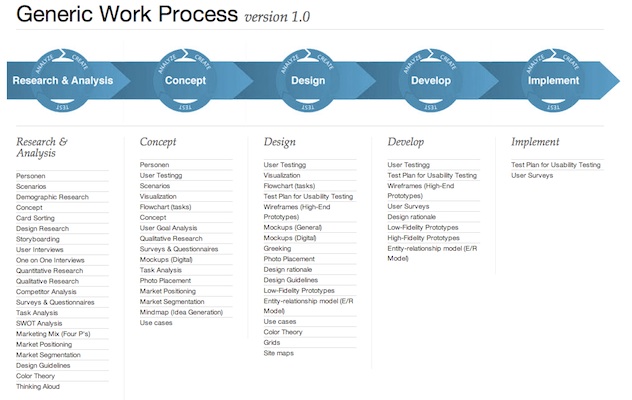
User-centered design: an updated recap
Source: Ritter, F. E., Baxter, G. D., & Churchill, E. F. (2014). Foundations for Designing User-Centered Systems: What System Designers Need to Know about People (2014 edition.). New York: Springer.
User-experience Design
Experience Design focuses on the need of designing the quality and the esthetics of the experiences that people live while interacting with an artifact, wether material or immaterial, physical or cognitive, putting on the first level the concept of user experience.
Source: Rizzo, F. (2009). Strategie di co-design : teorie, metodi e strumenti per progettare con gli utenti. Milano: F. Angeli.
User-experience Design
Two possible interpretations:
- experience design
- design based on the experience
Source: Rizzo, F. (2009). Strategie di co-design : teorie, metodi e strumenti per progettare con gli utenti. Milano: F. Angeli.
User-experience Design: approaches
- people-centered approaches: studying the individual experience
- product-centered approaches: studying the features of products that generate experience
- interaction-centered approaches: studying the interactions between people and artifacts
Source: Rizzo, F. (2009). Strategie di co-design : teorie, metodi e strumenti per progettare con gli utenti. Milano: F. Angeli.
User-experience Design: Emotions
Source: Norman, D. A. (2004). Emotional design why we love (or hate) everyday things. New York: Basic Books.
Emotions: how?
Emotions: how?
Source: http://www.themindensemble.com/tag/mind-processing-chair-emotiv-epoc-anton-rhino/
Emotions: how?

Source: http://www.wefeelfine.org/
User-experience Design: the role
Experience Design does not aim at understanding how products enter effectively into people's activities. This was the aim of UCD [...] UED tries to understand the deep meaning of how artifacts enter reflexively in relations with the users, of how people understand themselves in relation to the artifacts. Experience Design aims at an empathic understanding of the user [...] [the designer is] an interpreter. The role of an interpreter is to mediate the user experience inside a design process.
Source: Rizzo, F. (2009). Strategie di co-design : teorie, metodi e strumenti per progettare con gli utenti. Milano: F. Angeli.
Experience Design: Experience Economy

Source: Pine, B. J., & Gilmore, J. H. (1999). The experience economy work is theatre & every business a stage. Boston: Harvard Business School Press.
Co-Design
Co-design is defined as a form of collaboration aiming at design [...] It is a methodology for the designing with the users and not necessarily for the users.
Source: Rizzo, F. (2009). Strategie di co-design : teorie, metodi e strumenti per progettare con gli utenti. Milano: F. Angeli.
The landscape of human-centered design
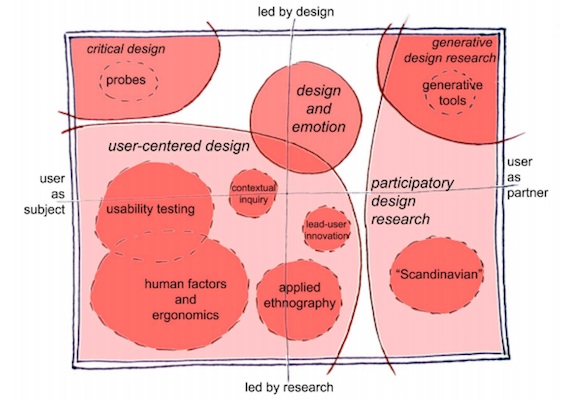
Source: Sanders, E., & Stappers, P. J. (2008). Co-creation and the new landscapes of design. CoDesign, 4(1), 5–18. doi:10.1080/15710880701875068
Co-Design & Co-creation
The authors take co-creation to refer to any act of collective creativity, i.e., creativity that is shared by two or more people.
By co-design we indicate collective creativity as it is applied across the whole span of a design process, as was intended by the name of this journal. Thus, co-design is a specific instance of co-creation.
Source: Sanders, E., & Stappers, P. J. (2008). Co-creation and the new landscapes of design. CoDesign, 4(1), 5–18. doi:10.1080/15710880701875068
Co-Design @ the Fuzzy Front End
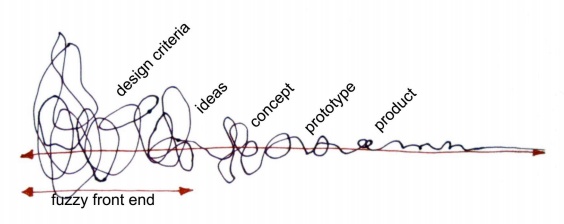
The goal of the explorations in the front end is to determine what is to be designed and sometimes what should not be designed and manufactured.
Source: Sanders, E., & Stappers, P. J. (2008). Co-creation and the new landscapes of design. CoDesign, 4(1), 5–18. doi:10.1080/15710880701875068
The limits of user-centered design
But it is now becoming apparent that the user-centered design approach cannot address the scale or the complexity of the challenges we face today. We are no longer simply designing products for users. We are designing for the future experiences of people, communities and cultures who now are connected and informed in ways that were unimaginable even 10 years ago.
Source: Sanders, E., & Stappers, P. J. (2008). Co-creation and the new landscapes of design. CoDesign, 4(1), 5–18. doi:10.1080/15710880701875068
Co-Design: change of role for designers
- User-centered Design: users are passive participants to be studied
- User-experience Design: users are experts of their experience, can then generate concepts, but designers will develop them in artifacts
- Co-Design: users as co-creator, designers as facilitators a nd researchers
Source: Rizzo, F. (2009). Strategie di co-design : teorie, metodi e strumenti per progettare con gli utenti. Milano: F. Angeli.
Probes: a toolkit
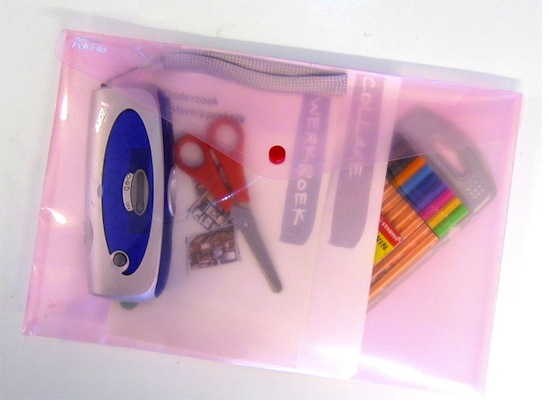

Probes: to gather information

Mattelmäki: "Probes"

Source: Mattelmäki, T. (2006). Design probes. Retrieved from https://www.taik.fi/kirjakauppa/product_info.php?products_id=28
Co-Design: Workshop
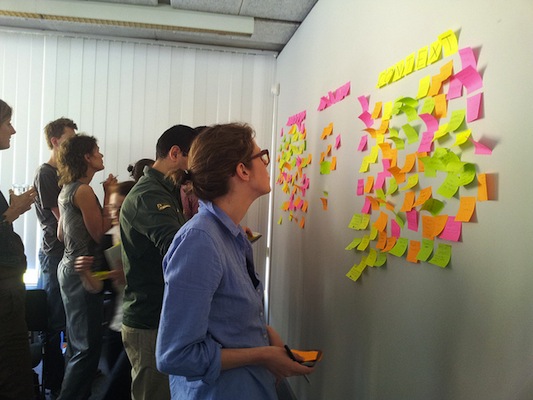

Source: http://www.flickr.com/photos/93570163@N02/9204754137/
User-centered Design, User Experience Design, Co-Design
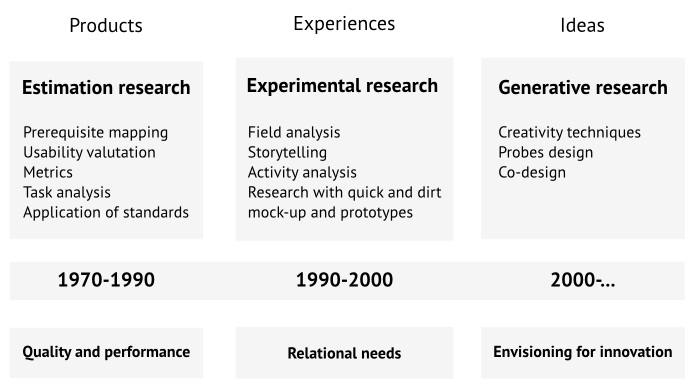
Source: Rizzo, F. (2009). Strategie di co-design : teorie, metodi e strumenti per progettare con gli utenti. Milano: F. Angeli.
Prototypes for User-centered Design, User Experience Design, Co-Design
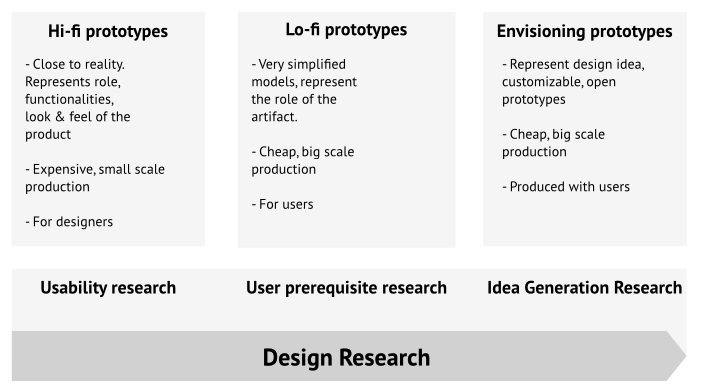
Source: Rizzo, F. (2009). Strategie di co-design : teorie, metodi e strumenti per progettare con gli utenti. Milano: F. Angeli.
Lunch time! Questions?
See you at 13:00
2. Lead users, Open Innovation and Open Source
von Hippel: "The sources of innovation"

Source: Von Hippel, E. (1988). The sources of innovation. New York: Oxford University Press. Retrieved from http://web.mit.edu/evhippel/www/sources.htm
von Hippel: "Democratizing Innovation"

Source: Von Hippel, E. (2005). Democratizing innovation. Cambridge Mass.: MIT Press. Retrieved from http://web.mit.edu/evhippel/www/democ1.htm
Lead Users: Skateboard
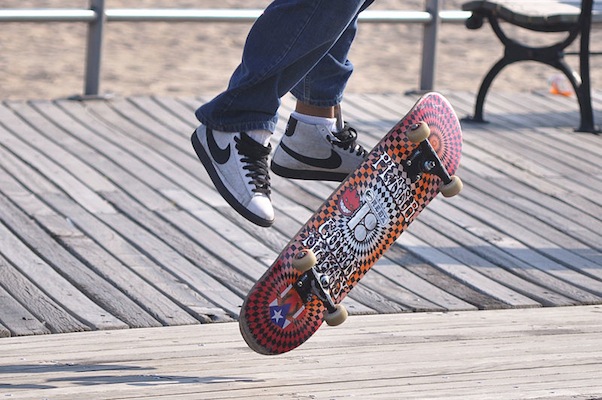

Source: http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Plan_B_(3598746031).jpg
Lead Users: Mountain Bike
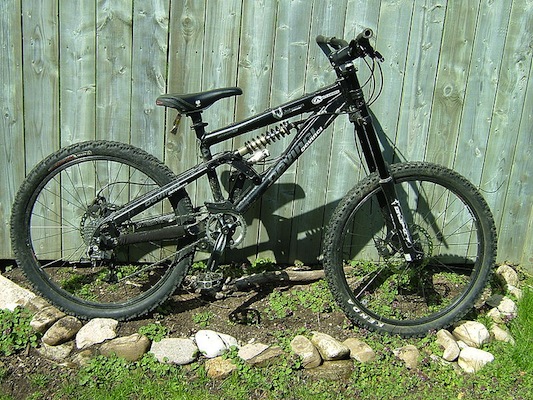

Source: http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Devinci_bike.JPG
von Hippel: Lego, User-Generated Innovation
von Hippel: Methodology for Lead Users
Source: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tNKrX1QxN6U&list=PLD4C0E9AEDF085119
Ladders of participation: Arnstein
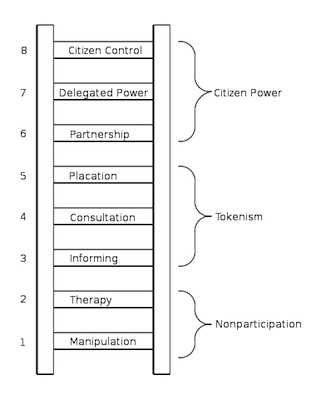
Source: Arnstein, S. R. (1969). A ladder of citizen participation. Journal of the American Institute of planners, 35(4), 216–224.
Ladders of participation: Hart

Source: Hart, R. A. (1997). Children’s participation: the theory and practice of involving young citizens in community development and environmental care. Earthscan. Retrieved from http://www.cabdirect.org/abstracts/20016783259.html
Ladders of participation: Forrester
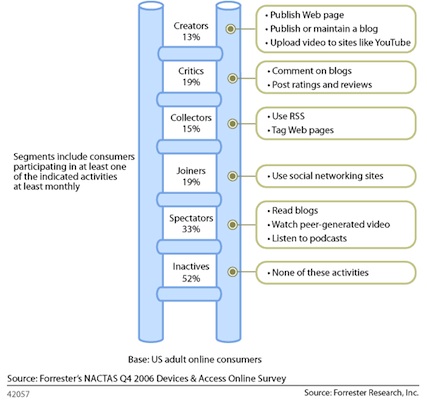
Source: NACTAS Q4 2006 Survey.
Ladders of participation: Web communities
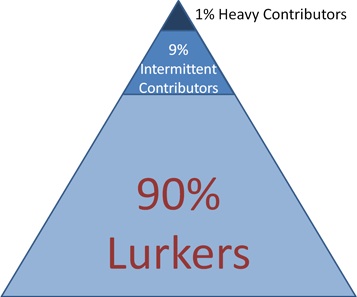
Source: http://www.nngroup.com/articles/participation-inequality/
Chesbrough: "Open Innovation"
Source: Chesbrough, H. W. (2003). Open Innovation: The New Imperative for Creating and Profiting from Technology. Harvard Business School Press.
Chesbrough: "Open Services Innovation"
Source: Chesbrough, H. (2011). Open Services Innovation: Rethinking Your Business to Grow and Compete in a New Era (1st ed.). Jossey-Bass.
Open Innovation: the concept
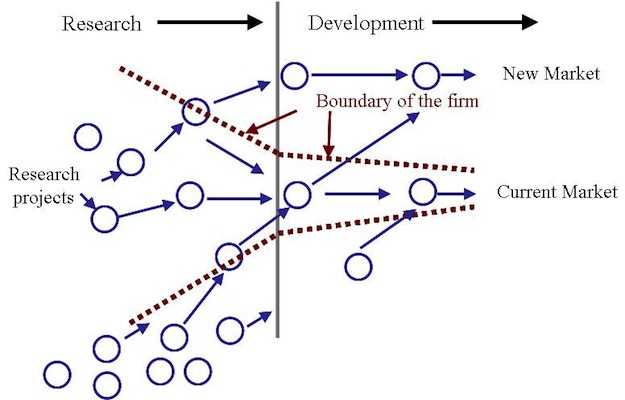
Source: http://www.crowdsourcing.org/editorial/open-innovation-creating-through-community-creation/16499
Open Innovation: Innocentive
Source: http://www.innocentive.com/
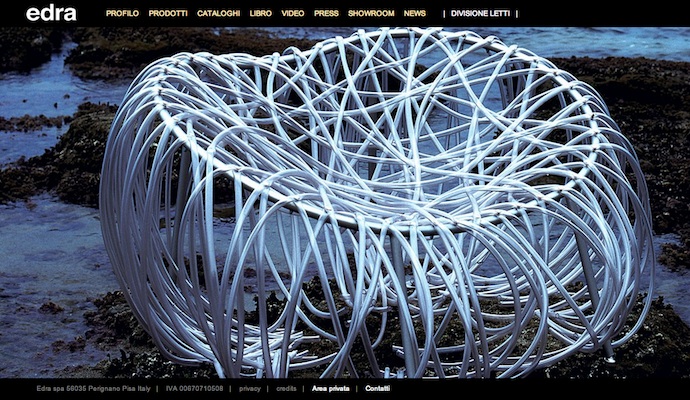
Open Innovation: Edra

Open Innovation: Santa&Cole
Source: http://www.santacole.com/en/catalogo/lamparas-de-sobremesa
Open Innovation: Santa&Cole
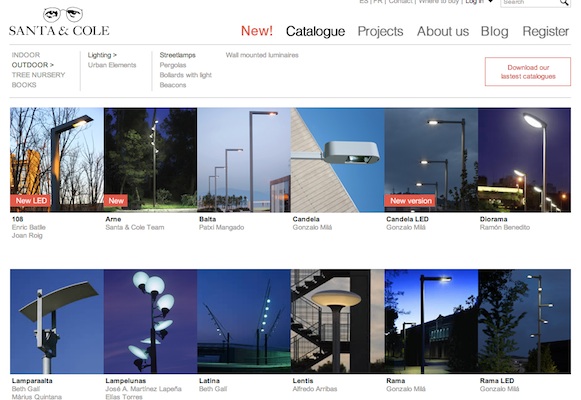
Open Innovation: Santa&Cole
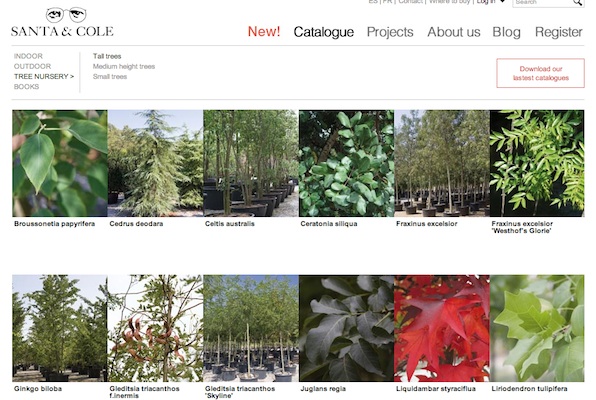
Source: http://www.santacole.com/en/catalogo/arboles-de-gran-desarrollo
Open Innovation: Santa&Cole
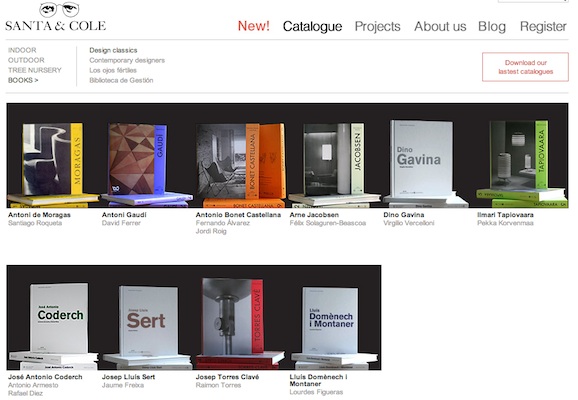
Source: http://www.santacole.com/en/catalogo/clasicos-del-diseno
Open Innovation: The Physical Internet
Open Source: what is it?
A (software) project published with a license that facilitates its access + modifying + sharing in a collaborative way.
A (software) project developed collaboratively by a community, based not on hierarchy but on reputation.
Open Source: what is it?
Source Code (human readable)
-->
Binary Code (machine readable)
Source Code

Binary Code

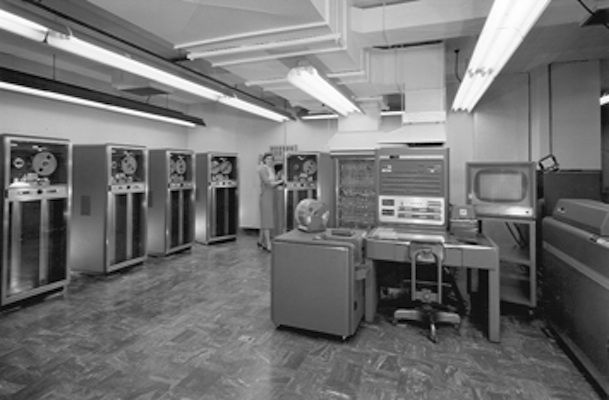
Back to history: Mainframes

Back to history: Proprietary Software

Source: http://content.time.com/time/covers/0,16641,19840416,00.html
RMS Stallman

Source: http://stallman.org/
GNU: "Gnu's Not Unix"

Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/GNU
Stallman: Free Software Definition
“Free software” means software that respects users' freedom and community. Roughly, the users have the freedom to run, copy, distribute, study, change and improve the software. With these freedoms, the users (both individually and collectively) control the program and what it does for them.
RMS Stallman
Stallman: The Four Freedoms
- The freedom to run the program, for any purpose (freedom 0).
- The freedom to study how the program works, and change it so it does your computing as you wish (freedom 1). Access to the source code is a precondition for this.
- The freedom to redistribute copies so you can help your neighbor (freedom 2).
- The freedom to distribute copies of your modified versions to others (freedom 3). By doing this you can give the whole community a chance to benefit from your changes. Access to the source code is a precondition for this.
Free Software Foundation
Source: http://www.fsf.org/
Stallman: "Free Software Free Society"

Source: Richard Stallman. (2010). Free Software, Free Society - Selected Essays of Richard M. Stallman, 2nd Edition. GNU Press. Retrieved from http://archive.org/details/FreeSoftwareFreeSociety-SelectedEssaysOfRichardM.Stallman2nd
Linus Torvalds

GNU/Linux

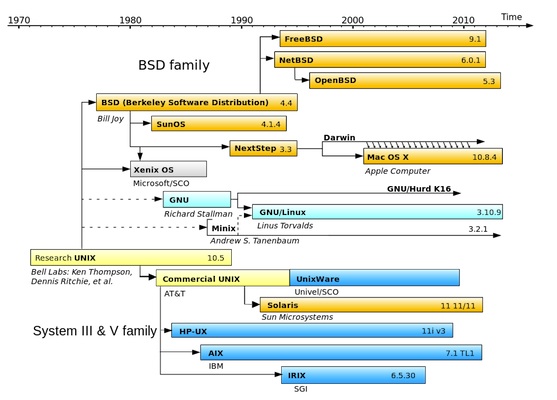
GNU/Linux: how it's made
Unix
GNU/Linux: Ubuntu
Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ubuntu_(operating_system)
GNU/Linux: Ubuntu
GNU/Linux: Ubuntu
GNU/Linux: Ubuntu on Android
GNU/Linux: Ubuntu Mobile
Source: http://youtu.be/aW8KVq52CYU
GNU/Linux: Ubuntu for Tablets
GNU/Linux: Ubuntu TV
Raymond: "The Cathedral and the Bazaar"

Source: Raymond, E. S. (2001). The Cathedral & the Bazaar: Musings on Linux and Open Source by an Accidental Revolutionary (Revised.). O’Reilly Media. Retrieved from http://www.catb.org/~esr/writings/cathedral-bazaar/
Kuwabara: "Linux: a Bazaar at the edge of chaos"

Source: Kuwabara, K. (2000). Linux: A Bazaar at the Edge of Chaos. First Monday, 5(3). Retrieved from http://firstmonday.org/article/view/731/640
Open Source Initiative
Source: http://opensource.org/
The Open Source Definition
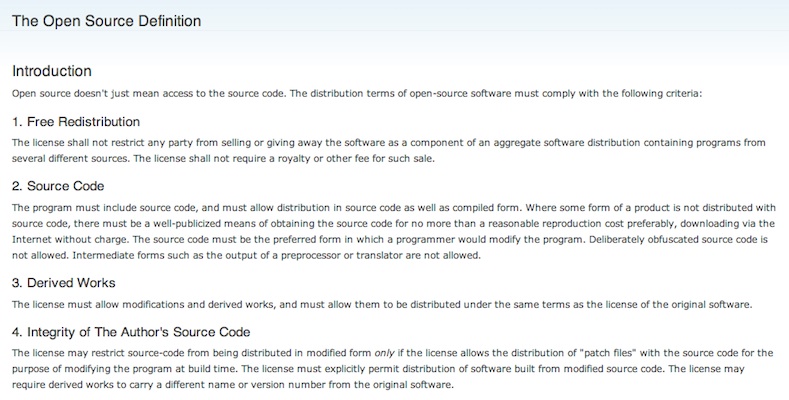
Source: http://opensource.org/osd
Open Source: LAMP Stack

Source: http://opensource.org/osd
Open Source Design software: Gimp
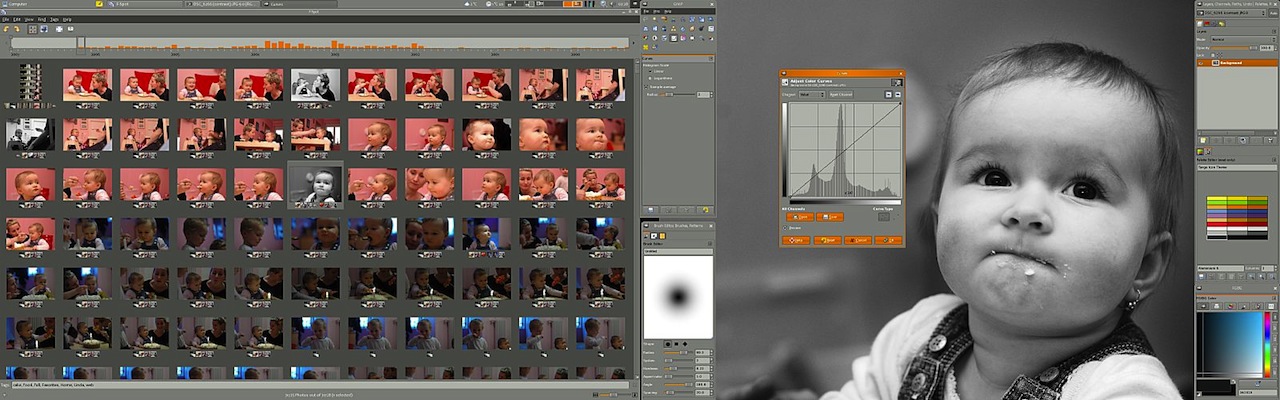
Source: http://www.gimp.org/
Open Source Design software: Inkscape
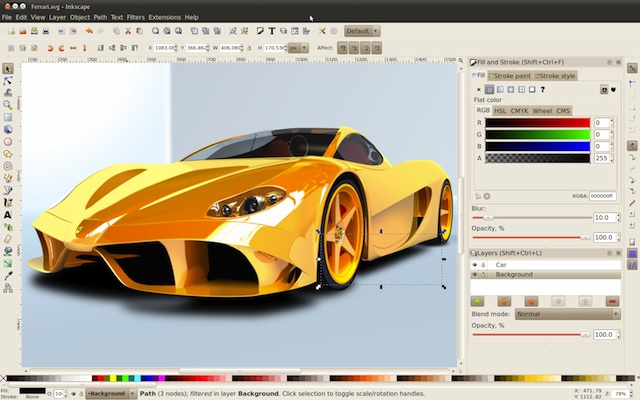
Source: http://www.inkscape.org/
Open Source Design software: Blender
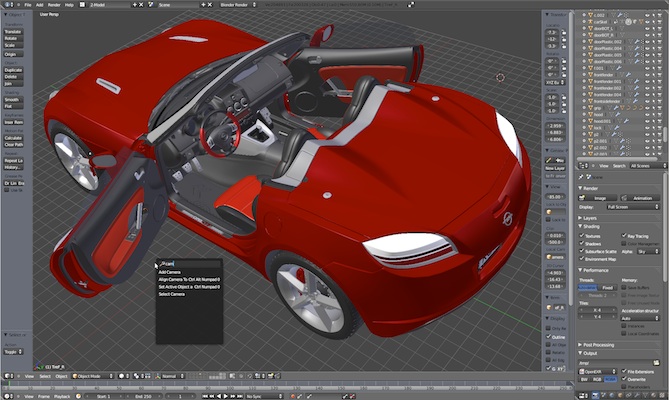
Source: http://www.blender.org/
Blender: Open Movies
Source: http://youtu.be/YE7VzlLtp-4
Open Source Design software: Scribus
Source: http://www.scribus.net/
Open Source and Co-Design
- Democratization of access, not necessarily of design
- By professionals, for professionals: Knowledge intensive
- Yes, if there are designers... but relationships should be redefined
- ...
Open Source vs. Open Innovation
“Open innovation is sometimes confated with open source methodologies for software development. There are some concepts that are shared between the two, such as the idea of greater external sources of information to create value. However, open innovation explicitly incorporates the business model as the source of both value creation and value capture. This latter role of the business model enables the organization to sustain its position in the industry value chain over time. While open source shares the focus on value creation throughout an industry value chain, its proponents usually deny or downplay the importance of value capture.”
Source: Chesbrough, H. (2011). Open Services Innovation: Rethinking Your Business to Grow and Compete in a New Era (1st ed.). Jossey-Bass.
Open Data: a related issue

Source: http://opendefinition.org/
Open Data: which kind of data?
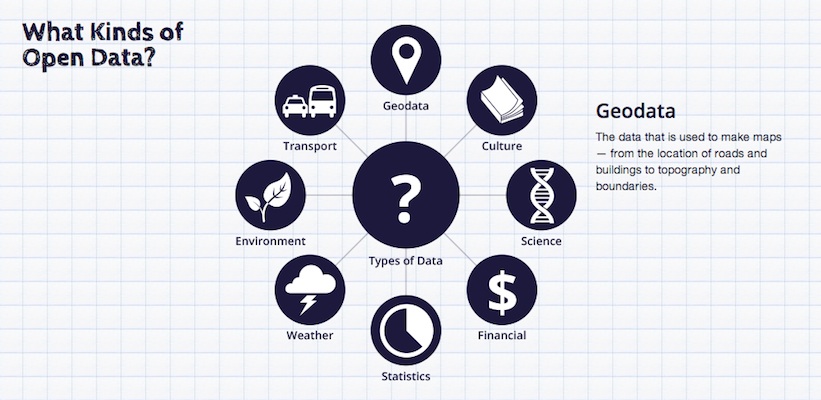
Source: http://okfn.org/opendata/
Open Data: a handbook

Source: http://opendatahandbook.org/
Open Data: an example
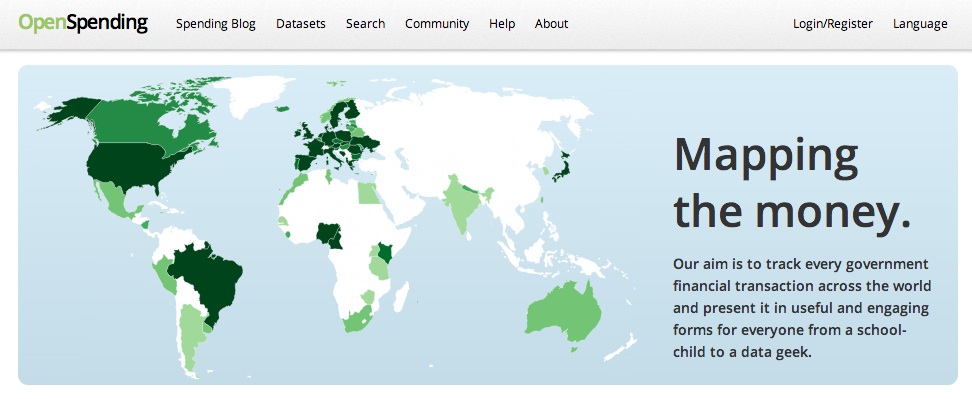
Source: http://openspending.org/
Open Data: Open Knowledge Foundation
Source: http://okfn.org/
Big Data vs Open Data vs Open Government
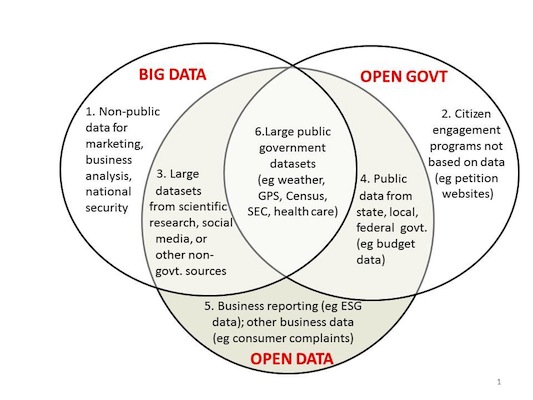
Source: http://www.opendatanow.com/2013/11/new-big-data-vs-open-data-mapping-it-out/
Thank you!
Massimo Menichinelli / info@openp2pdesign.org / @openp2pdesign

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License.
Massimo Menichinelli 2014-2015
openp2pdesign.org
